What is EPDM: The Ultimate Guide for it
What is EPDM: The Ultimate Guide for it
You may have heard of EPDM rubber when looking into what materials to use for your sealing products. It’s a common synthetic rubber that is extremely durable and flexible, leading to a wide range of applications.
In this article, we’re going to tell you what you need to know about the EPDM material.
Introduction: What is EPDM?
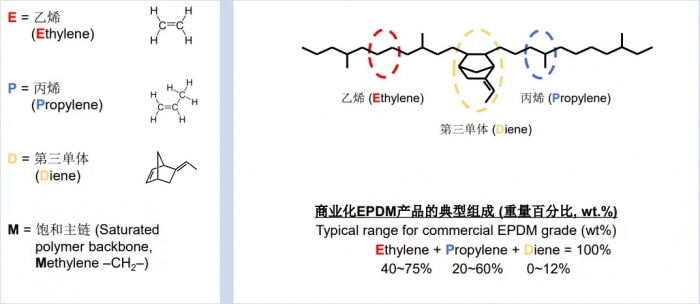
EPDM stands for Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer. Because it’s such a tongue twister, it’s usually referred to as EPDM rubber or just EPDM. The rubber is composed from three monomers: ethylene, propylene, and diene. The rubber is mostly ethylene, with this component making up between 45%-75% of the material. The rest is propylene and diene, although diene is usually only a small percentage of the material. Diene gives EPDM its resilience, flexibility, and durability. The combination of the three materials together is what make EPDM such a powerful copolymer.
Standard EPDM is usually sulfur cured for improved flexibility. EPDM can also be peroxide cured to ensure better heat resistance and a lower (lower means better) compression set. The material is also sometimes coated for easier installation and reduced friction.
Advantages of EPDM
EPDM has excellent ozone, sunlight, and weathering resistance and very good flexibility at low temperatures. It is one of the best materials to withstand cold temperatures because of its compression properties and resistance to tears. It also has great chemical resistance and electrical insulation properties.
The compound performs well in alcohols, ketones, dilute acids, alkalis, and silicone oils and grease. It can withstand steam up to 204°C (400°F), water, and phosphate ester-based hydraulic fluids. It is also very durable and has great resistance to aging.
Disadvantages of EPDM
While EPDM is a very versatile compound, it can’t be used in every situation. The rubber is susceptible to aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons, di-ester-based lubricants, halogenated solvents, and petroleum-based oils and grease. It has no resistance to hydrocarbon fluids and is susceptible to corrosion should it come in contact. These properties mean it isn’t a good choice for oil and gas applications.
EPDM Chemical Compatibility and Unique Properties
EPDM is compatible with many chemicals, especially at high or extremely low temperatures. This is one of the properties that makes EPDM so unique. It is compatible with polar fluids, solvents, as well as the materials previously mentioned. It also has very low water absorption, making it a good barrier against water and water vapor. In fact, it is one of the most waterproof rubbers available. For these reasons, EPDM is very durable and offers excellent protection in sealing products.
Let’s look at some of EPDM’s material properties:
| Temperature resistance for Standard Compound | -40°C (-40°F) to 125°C (257°F) |
| Temperature resistance for Special Compound | -55°C (-67°F) to 150°C (302°F) |
| Hardness | 30 to 90 Shore A |
| ASTM D1418 Designation | EPM, EPDM |
| ASTM D2000 Designation | AA, BA, CA, DA |
| Standard Color for shelf items | Black |
Looking for EPDM Seals?
EPDM seals could be a great choice for your business. Techno Ad distribute and manufactures many different types of O-rings, gaskets, and diaphragms from various EPDM compounds.
We can help you design EPDM seals for your specific requirements.
Are you interested in learning more? Contact us today via kent.wei@isunled.com. We’d be happy to help!





 Send Email
Send Email